Gallbladder stones, or gallstones, affect millions of people worldwide, yet myths about them often create confusion and fear. Understanding the facts can help you make better health choices and seek the right care. Let’s clear up some of the most common myths and provide accurate information about gallstones. For expert advice, consulting a gastroenterologist in Surat can offer the clarity and care you need.
What Are Gallstones?
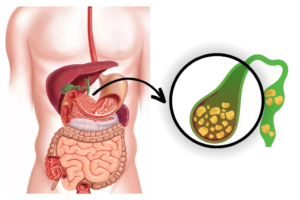
Gallstones are small, hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, a tiny organ under the liver. They develop when substances like cholesterol, bile salts, or calcium mix in an unhealthy way. These stones vary in size, from a grain of sand to as big as a golf ball.
Not all gallstones cause symptoms, but when they do, they can lead to discomfort and complications, making it important to separate fact from fiction.
Myth 1: Gallstones Only Happen to Older Adults
Fact: While gallstones are more common in people over 40, they can occur at any age. Young adults, teenagers, and even children can develop gallstones, especially if they have risk factors like obesity, poor diet, or a family history of the condition.
Risk Factors Include:
- Being overweight or obese.
- Eating a diet high in unhealthy fats.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy or while taking hormonal therapy.
Myth 2: Gallstones Always Cause Pain
Fact: Many people with gallstones experience no symptoms at all. These “silent” gallstones don’t interfere with gallbladder function and are often found by chance during medical tests for other issues.
When Pain Does Occur:
- It’s usually in the upper right abdomen and can radiate to the back or right shoulder.
- Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and indigestion.
If the pain is severe or persistent, it’s a sign to seek medical help promptly.
Myth 3: A Low-Fat Diet Prevents Gallstones
Fact: While eating less unhealthy fat is beneficial for your health, it won’t completely eliminate the risk of gallstones. Your body actually needs some healthy fats to keep the gallbladder functioning properly.
Better Prevention Tips:
- Maintain a balanced diet with fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Incorporate healthy fats like nuts, seeds, and olive oil into your meals.
Myth 4: You Can Dissolve Gallstones with Home Remedies
Fact: Natural remedies like apple cider vinegar or herbal teas may sound appealing, but there’s no scientific evidence that they can dissolve gallstones. Relying on unproven methods can delay proper treatment and worsen the condition.
Proven Treatments Include:
- Medications for small cholesterol stones.
- Surgery (gallbladder removal) for symptomatic or severe cases.
Always consult a doctor before trying any remedies for gallstones.
Myth 5: Surgery Is the Only Option
Fact: Not every case of gallstones requires surgery. If the stones are small and asymptomatic, your doctor might suggest monitoring them instead of immediate treatment.
Treatment Options:
- Medications: These can help dissolve certain types of stones.
- Surgery: Recommended for recurring or severe symptoms to prevent complications like infections or bile duct blockages.
Myth 6: Gallstones Are Always Caused by an Unhealthy Diet
Fact: Diet is just one of many factors that contribute to gallstones. Genetics, rapid weight loss, and certain medical conditions like diabetes or liver disease also play significant roles.
Key Triggers to Watch For:
- Losing weight too quickly through crash diets.
- Hormonal imbalances due to pregnancy or birth control pills.
Myth 7: Gallstones Are All the Same
Fact: Gallstones vary in type and composition. The two main types are:
- Cholesterol Stones: The most common, usually yellow or green.
- Pigment Stones: Made of bilirubin, more common in people with liver disease.
Knowing the type of gallstones can help your doctor decide the best treatment for you.
Myth 8: Life After Gallbladder Surgery Is Difficult
Fact: Most people live normal, healthy lives after gallbladder removal. Your liver continues to produce bile, which aids digestion, even without the gallbladder.
Post-Surgery Tips:
- Avoid fatty, greasy foods for a few weeks after surgery.
- Gradually reintroduce fiber-rich foods to your diet.
Any temporary digestive issues usually resolve within a few months.
When to See a Doctor
Gallstones don’t always need treatment, but certain symptoms signal it’s time to see a doctor, such as:
- Persistent or severe abdominal pain.
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice).
- Fever or chills, which could indicate an infection.
A doctor will use imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans to confirm the diagnosis and recommend treatment tailored to your condition.
Final Thoughts
Gallstones are a manageable condition, but the myths surrounding them can make people delay proper care. Understanding the facts helps you make informed decisions about your health.
For individuals in Gujarat, consulting a trusted gastroenterologist in Surat ensures you get expert care and advice tailored to your needs. Don’t let myths hold you back from living a healthier, pain-free life.
